Introduction
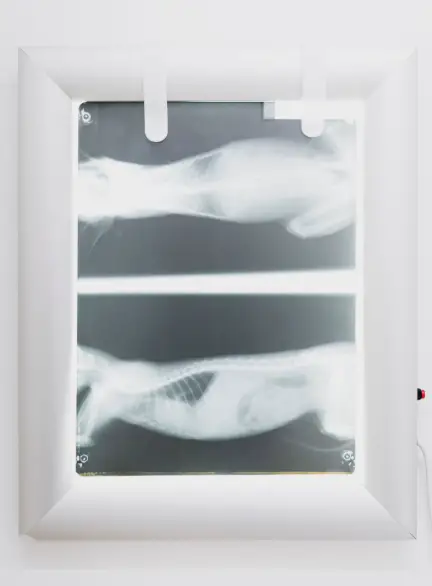
A remarkable medical case recently published in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine has brought attention to an unexpected discovery that highlights both the complexity of alternative medicine practices and the potential complications that can arise from unconventional treatment approaches. The case involves a 65-year-old South Korean woman whose X-ray examination revealed hundreds of tiny gold acupuncture needles embedded in her knee tissue, creating what medical professionals described as a “gold mine” appearance on radiological imaging.
Patient Background and Initial Diagnosis
The patient in question had been living with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Osteoarthritis represents one of the most common forms of arthritis, characterized by the progressive breakdown of cartilage and bone tissue within joints. This condition typically results in significant pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, particularly affecting weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine.
For individuals suffering from osteoarthritis, the search for effective pain management often becomes a central focus of their healthcare journey. Traditional treatment approaches typically begin with conventional pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications, which aim to reduce both pain and the inflammatory response associated with joint degeneration.
Treatment Challenges and Alternative Approaches
In this particular case, the patient experienced a common dilemma faced by many arthritis sufferers: conventional pharmaceutical treatments proved inadequate for managing her pain levels while simultaneously causing undesirable gastrointestinal side effects. This scenario frequently leads patients to explore alternative treatment modalities, seeking relief through non-traditional medical approaches.
The patient’s experience with stomach discomfort from anti-inflammatory medications is not uncommon. These drugs, while effective for many patients, can cause significant gastrointestinal irritation, ulcers, and other digestive complications, particularly with long-term use. This side effect profile often motivates patients to seek alternative pain management strategies.
Understanding Acupuncture as Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture, the treatment method chosen by this patient, represents one of the oldest and most widely practiced forms of alternative medicine. Originating in ancient China over 2,000 years ago, acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body, known as acupoints. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, these points lie along pathways called meridians, through which vital energy, or “qi,” flows.
From a modern medical perspective, researchers have proposed various mechanisms by which acupuncture might provide pain relief, including the stimulation of endorphin release, modulation of pain signals in the nervous system, and potential anti-inflammatory effects. However, the scientific evidence supporting acupuncture’s effectiveness remains a subject of ongoing debate within the medical community.
The Gold Needle Technique: Cultural Context and Practice
The specific technique employed in this case involved the use of gold acupuncture needles, which were intentionally left embedded in the patient’s tissue for sustained therapeutic effect. This practice, while uncommon in Western medicine, represents a traditional approach used in various Asian countries, particularly for treating arthritis and joint pain.
Gold needle acupuncture, sometimes referred to as “implant acupuncture” or “permanent acupuncture,” involves placing small pieces of sterile gold wire or thread at specific acupoints. Practitioners believe that leaving these materials in place provides continuous stimulation to the treatment points, potentially offering longer-lasting therapeutic benefits compared to traditional temporary needle insertion.
Medical Concerns and Professional Opinions
The discovery of hundreds of embedded needles raised significant concerns among medical professionals. Dr. Ali Guermazi, a distinguished professor of radiology at Boston University who was not involved in the original case, provided expert commentary on the potential risks associated with leaving foreign objects in the body.
According to Dr. Guermazi, the human body’s natural response to foreign materials involves inflammatory processes designed to isolate and eliminate these objects. This biological response can lead to several complications, including chronic inflammation, abscess formation, and increased risk of infection. The body’s attempt to encapsulate foreign objects through fibrous tissue formation can also create additional complications over time.
Diagnostic and Treatment Implications
From a diagnostic standpoint, the presence of numerous metallic objects in the body creates significant challenges for healthcare providers. X-ray imaging, a fundamental diagnostic tool for assessing joint conditions, can become difficult to interpret when foreign objects obscure anatomical structures. This interference can potentially mask important pathological changes or make it challenging to monitor disease progression accurately.
Perhaps more concerning are the limitations imposed on future medical care. The presence of metallic needles in the body creates contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating soft tissue conditions. The strong magnetic fields used in MRI procedures can cause metallic objects to move within the body, potentially damaging blood vessels, nerves, or other critical structures.
Statistical Context and Usage Patterns
The popularity of acupuncture as an alternative treatment option is reflected in usage statistics from health organizations. According to data from the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, approximately 3.1 million American adults and 150,000 children received acupuncture treatments in 2007. These numbers likely represent a conservative estimate, as alternative medicine usage has continued to grow in subsequent years.
The widespread adoption of acupuncture treatments underscores the importance of understanding both potential benefits and risks associated with these practices. While many patients report positive experiences with acupuncture, cases like the one documented in the New England Journal of Medicine highlight the need for careful consideration of treatment protocols and potential long-term consequences.
Evidence-Based Medicine Perspective
The scientific medical community maintains a cautious stance regarding acupuncture’s therapeutic claims. While some studies have suggested potential benefits for certain conditions, particularly pain management, the overall body of evidence remains insufficient to definitively establish acupuncture’s effectiveness for most medical conditions.
High-quality randomized controlled trials, considered the gold standard for medical research, have produced mixed results regarding acupuncture’s efficacy. Some studies suggest modest benefits for specific types of chronic pain, while others show no significant difference compared to placebo treatments or conventional care.
Patient Safety and Informed Consent
This case emphasizes the critical importance of patient safety considerations and informed consent in alternative medicine practices. Patients considering acupuncture treatments, particularly those involving permanent needle placement, should be thoroughly informed about potential risks, benefits, and long-term implications.
Healthcare providers and acupuncture practitioners share the responsibility of ensuring that patients understand the full scope of their treatment choices, including potential complications and limitations on future medical care. This collaborative approach helps patients make informed decisions that align with their healthcare goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion and Clinical Implications
The South Korean patient’s case serves as a valuable educational example for both medical professionals and patients considering alternative treatment approaches. While the search for effective pain management solutions is understandable, particularly for chronic conditions like osteoarthritis, this case demonstrates the importance of carefully weighing potential benefits against possible risks.
As the field of integrative medicine continues to evolve, cases like this contribute to our understanding of how traditional and alternative practices can impact modern healthcare delivery. The medical community’s ongoing evaluation of these practices, combined with rigorous scientific investigation, will ultimately help establish evidence-based guidelines for safe and effective patient care.
For patients suffering from chronic pain conditions, this case underscores the importance of working closely with qualified healthcare providers to develop comprehensive treatment plans that consider both conventional and alternative approaches while prioritizing patient safety and long-term health outcomes.

Adrian Hawthorne is a celebrated author and dedicated archivist who finds inspiration in the hidden stories of the past. Educated at Oxford, he now works at the National Archives, where preserving history fuels his evocative writing. Balancing archival precision with creative storytelling, Adrian founded the Hawthorne Institute of Literary Arts to mentor emerging writers and honor the timeless art of narrative.