Diane Keaton’s Cause of Death Confirmed as Pneumonia — Understanding the 15 Warning Signs of This Silent Killer
Hollywood is mourning the loss of one of its most beloved icons. Diane Keaton, the Oscar-winning actress and star of The Godfather and Annie Hall, has died at the age of 79, her family confirmed. The cause of death: pneumonia, a lung infection that remains one of the most serious respiratory illnesses in the world.

The announcement, made through a statement shared with People, revealed that Keaton passed away in California on Saturday, October 11, surrounded by loved ones. Emergency responders from the Los Angeles Fire Department were dispatched to her home shortly after 8 a.m., but despite their efforts, she was pronounced dead at the scene.
“The Keaton family are very grateful for the extraordinary messages of love and support they have received these past few days on behalf of their beloved Diane, who passed away from pneumonia on October 11,” the statement read.
“She loved her animals and was steadfast in her support of the unhoused community, so any donations in her memory to a local food bank or animal shelter would be a wonderful and much appreciated tribute to her.”
The news of her passing has sparked an outpouring of tributes from fans, friends, and co-stars across the world. Known for her quirky humor, elegance, and effortless charisma, Diane Keaton leaves behind not just an impressive legacy in cinema but also a quiet message about the dangers of pneumonia — a disease that can strike unexpectedly, even in the healthiest of individuals.
A Legendary Career Remembered
Diane Keaton first captured global attention through her unforgettable role as Kay Corleone in The Godfather trilogy, portraying the conflicted wife of Michael Corleone with a rare blend of strength and vulnerability. She later won the Academy Award for Best Actress for her performance in Annie Hall (1977), solidifying her as one of Hollywood’s most versatile and enduring talents.
Over her decades-long career, Keaton starred in countless hits — from Something’s Gotta Give and Baby Boom to The First Wives Club — shaping generations of audiences with her authenticity and charm. But beyond the screen, she was an animal lover, philanthropist, and advocate for those without homes, often using her platform to highlight causes close to her heart.
Her death has not only left a void in the entertainment industry but has also drawn attention to the hidden severity of pneumonia, a condition that hospitalizes over one million Americans each year and claims the lives of around 50,000 people annually, according to UCLA Health.
What Is Pneumonia — and Why Is It So Dangerous?

Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing them to fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult and reducing oxygen levels in the bloodstream. According to experts from the Cleveland Clinic, the illness can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and it can range from mild to life-threatening.
The most common form — bacterial pneumonia — often stems from the Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterium. However, pneumonia can also develop as a complication of other respiratory illnesses, such as the flu, COVID-19, or the common cold.
In some cases, the body’s own immune response can worsen the condition, attacking the infection inside the tiny air sacs known as alveoli. When this happens, inflammation spreads quickly, leading to fever, chest pain, and respiratory distress.
Who Is Most at Risk?
While pneumonia can affect anyone, certain groups are more vulnerable. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) warns that people aged 65 or older, those with chronic heart or lung conditions, smokers, and pregnant women face a significantly higher risk of developing serious complications.
Other risk factors include:
-
Weakened immune systems due to illness or medication
-
Hospitalization or long-term care stays
-
Exposure to infectious agents in crowded environments
-
Pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD
15 Symptoms of Pneumonia Everyone Should Recognize
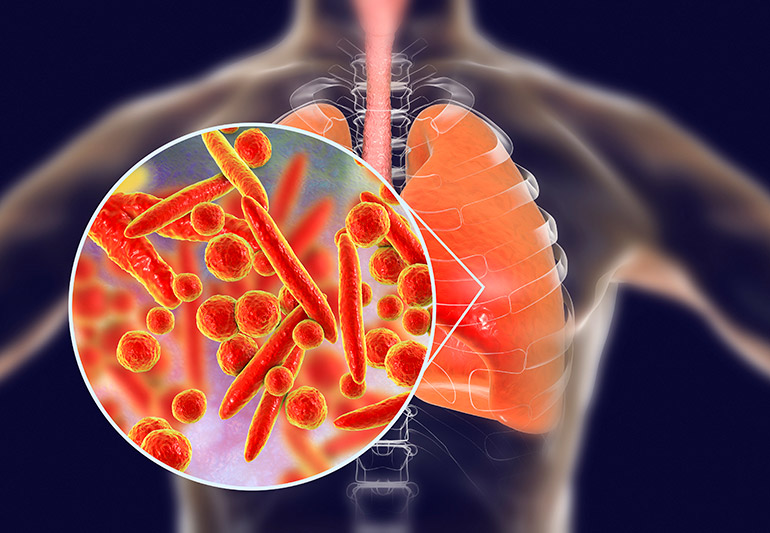
Pneumonia symptoms can vary based on whether the infection is bacterial or viral — but in both cases, early detection is key. Below are the 15 most common warning signs associated with pneumonia:
-
High fever — Often reaching temperatures up to 105°F (40.5°C)
-
Loss of appetite — A common early symptom due to fatigue and nausea
-
Excessive sweating or chills — The body’s immune system fighting infection
-
Rapid breathing — Caused by inflammation and fluid in the lungs
-
Shortness of breath — Especially noticeable during light activity or rest
-
Persistent cough — Sometimes producing yellow, green, or bloody mucus
-
Chest pain — Sharp or stabbing sensations that worsen when breathing deeply
-
Abdominal pain — Especially near the diaphragm or lower ribs
-
Rapid heart rate — The heart works harder to deliver oxygen
-
Blue-tinted lips or nails — A sign of low oxygen levels
-
Extreme fatigue — Weakness that persists even after rest
-
Confusion or disorientation — Particularly common in older adults
-
Headache and dizziness — Caused by fever and oxygen deprivation
-
Muscle pain — A common symptom in viral pneumonia
-
Dry cough and weakness — Especially prevalent in viral infections
Experts emphasize that pneumonia can begin subtly — resembling a bad cold or flu — and quickly escalate into a life-threatening emergency. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
How Pneumonia Is Diagnosed and Treated
Doctors typically diagnose pneumonia through a physical exam, chest X-rays, and blood tests to identify the infection type. In some cases, a CT scan or sputum test may be used for confirmation.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
-
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics
-
Viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications or supportive care
-
Fungal pneumonia is treated with antifungal drugs
Patients are also encouraged to rest, stay hydrated, and use fever-reducing medication. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for oxygen therapy or intravenous treatment.
A Silent Epidemic Hidden in Plain Sight
Despite being preventable and treatable, pneumonia continues to claim thousands of lives each year. Health professionals urge people — especially those over 60 — to get vaccinated and maintain regular flu and COVID boosters, which can lower the risk of respiratory infections that lead to pneumonia.
Simple habits like washing hands, avoiding smoking, and staying active can also significantly strengthen the lungs and immune system.
A Legacy Beyond the Screen
As the world remembers Diane Keaton for her grace, humor, and timeless performances, her passing also serves as a somber reminder of pneumonia’s dangers.
She will forever be remembered as the strong yet sensitive Kay Corleone, the witty Annie Hall, and the radiant woman who redefined charm in every role she touched. Her family’s statement captures the essence of who she was — compassionate, humble, and full of heart.
“She loved her animals and supported the unhoused community,” they shared. “In her memory, we ask that anyone wishing to honor her do so by giving to a local food bank or animal shelter — causes she cared about deeply.”
In the wake of her death, the message is clear: life is fragile, and awareness saves lives. Pneumonia may start with a cough — but left unchecked, it can take even the brightest stars from us far too soon.

Adrian Hawthorne is a celebrated author and dedicated archivist who finds inspiration in the hidden stories of the past. Educated at Oxford, he now works at the National Archives, where preserving history fuels his evocative writing. Balancing archival precision with creative storytelling, Adrian founded the Hawthorne Institute of Literary Arts to mentor emerging writers and honor the timeless art of narrative.
